ALIA’S BRAIN IS NEURAL MACHINE TRANSLATION (NMT)
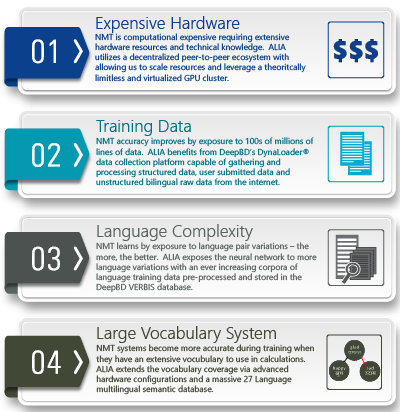
The rise of Neural Machine Translation over the past several years is a serious game changer. In a short time span, NMT has achieved accuracy rates equal to or better than existing statistical translation systems. Neural networks hold the promise of learning and understanding language in a way similar to the human brain – they learn by example from huge volumes of training data. Simply put, neural networks are not so much programmed as they are taught. However, NMT translation accuracy requires astronomical amounts of data and very significant hardware resources.
Moreover, neural networks continuously improve with experience – the more data they are fed, the more accurate and complete their response. Achieving an elevated level of translation accuracy requires astronomical amounts of translated document pairs and significant hardware resources. During training, a neural net continually readjusts thousands of internal parameters until it can reliably perform text translation from one language to another. Accuracy increases with the number of documents provided to the system. In most instances, these resource requirements are too expensive for most academic environments and small business, and therefore limit the speed of research.
ALIA advances the technology and overcomes 4 major challenges to implementing a powerful NMT solution that provides accuracy and allows for worldwide application.
In the coming years, AI technology will power the tools LSPs need to meet the fast-growing global demand for language services. Technological language services only made up 2.8% of the market in 2015, but that share doubled to 5.6% in 2016. The submarket for machine translations is growing at 20% YoY, and is projected to reach $2.3 billion by 2023.
Buyers of translation services are asking for faster turnaround times, more machine translations, and are already expecting an increasing role of AI technologies in the services they consume. The vendors that will benefit most from the robust growth in demand are those who will effectively leverage technology to deliver the cheaper, faster, highly accurate translations that almost all customers want. Historically, machine translations have occupied only a small percentage of the market because the technology has not existed to produce accurate translations on a grand scale. Growth in the machine translation submarket will only be limited by the speed at which technology improves.
At the present, large companies like Google and Facebook are pioneering NMT projects but operate as a “black-box” or “closed-source” translation service. This proprietary approach is true across most of the language translation industry, where translation companies refuse to democratize their translation technology capabilities. Although some firms in the translation industry have begun research into NMT, large companies like Google and Facebook still have a natural advantage when it comes to improving neural net technology for machine translation due to their endless R&D budgets and access to huge volumes of training materials.
The industry’s stakeholders understand and agree that the path to producing these cheaper, faster, highly accurate translations at scale is through NMT. NMT technology is quickly displacing the incumbent technologies powering machine translations, such as Statistical Machine Translation (SMT). Advances in NMT have only recently made the technology worth investing in and deploying to generate highly accurate translations. The relatively nascent, yet undeniably influential, role of NMT in the language services industry creates an enormous opportunity for early NMT adopters and innovators to capture significant market share.